
- SSH PROXY SERVER WINDOWNS MANUAL
- SSH PROXY SERVER WINDOWNS PLUS
- SSH PROXY SERVER WINDOWNS SERIES
- SSH PROXY SERVER WINDOWNS DOWNLOAD
- SSH PROXY SERVER WINDOWNS WINDOWS
The general connection scheme is shown below. SOCKS Proxy Server F - Secure SSH Client supports connecting through SOCKS Version 4 proxy servers.
SSH PROXY SERVER WINDOWNS WINDOWS
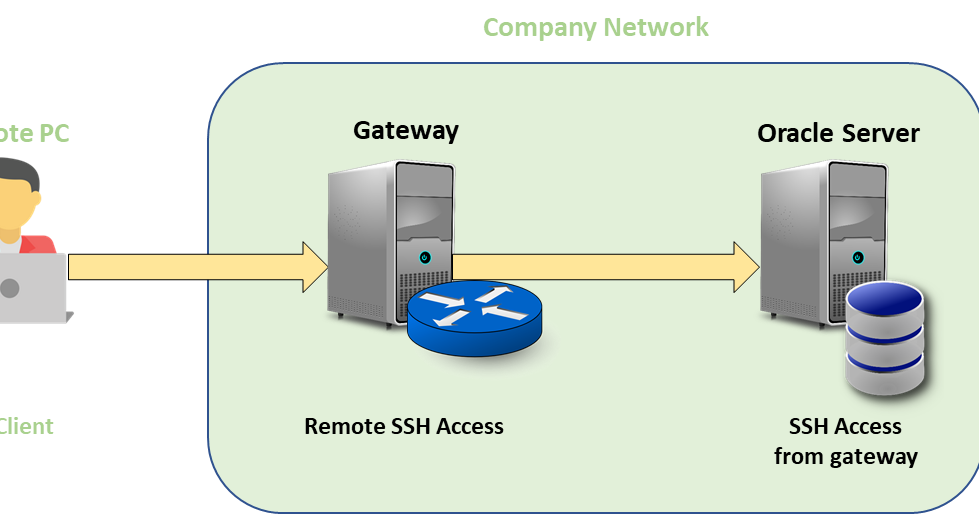
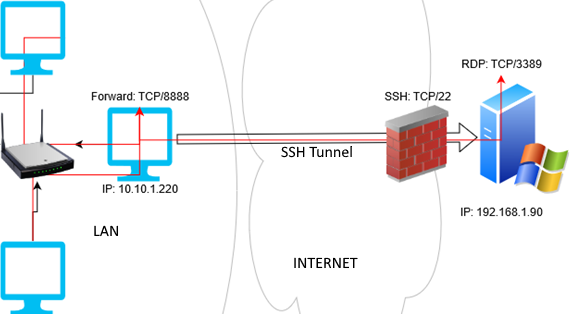
In this example, we will create a local Port 8888, and the connection to it will be forwarded to the RDP port 3389 on a remote Windows computer. All connections to this port are forwarded to the specified port on a remote server via the SSH tunnel. In this mode, you create a local TCP port on your computer. RDP Access Through SSH Tunnel (Local TCP Forwarding) Double SSH tunnel connects computers without any dedicated pubic IP addresses behind NAT through an SSH server (if OpenVPN solution is not applicable).Remote TCP forwarding is a remote port forwarding to a local computer.Local TCP forwarding is a local port forwarding to a remote server.Here are the typical usage scenarios of SSH tunneling: However, you can use the port forwarding technique through the SSH tunnel. It seems impossible since Remote Desktop port 3389 is blocked by the firewall. Your task is to connect to the Windows Server using the RDP client. All other ports are blocked by a hardware firewall or Windows Firewall. For example, you have a Windows Server with only SSH port open (TCP 22).
SSH PROXY SERVER WINDOWNS MANUAL
Check out ssh's manual page ( man ssh) sometime to discover all of the different options available with this seemingly simple program.SSH tunneling is mostly used in the scenarios when you need to connect to a remote computer behind the firewall. While it might mostly be used in its simplest form, ssh there are literally dozens of uses, with flags and configurations to make connections from one host to another. With this setting in ~/.ssh/config, any ssh connection to the remote host is accomplished by forwarding stdin and stdout through a secure connection from bastion-host. Prox圜ommand in ~/.ssh/configĪs with ProxyJump, Prox圜ommand can be set in the ~/.ssh/config file for hosts that always use this configuration: Host remote-host The %h:%p arguments to the -W flag above specify to forward standard in and out to the remote host ( %h) and the remote host’s port ( %p). The Prox圜ommand itself is a specific command used to connect to a remote server-in the case of the earlier example, that would be the manual ssh command used to first connect to the bastion: $ ssh -o Prox圜ommand="ssh -W %h:%p bastion-host" remote-host
Prox圜ommand works by forwarding standard in (stdin) and standard out (stdout) from the remote machine through the proxy or bastion hosts. ProxyJump is the simplified way to use a feature that ssh has had for a long time: Prox圜ommand. An alternative: Forwarding stdin and stdout The ssh command first creates a connection to the bastion host bastion-hostname (the host referenced, by nickname, in the remote host’s ProxyJump settings) before connecting to the remote host. Using the example configuration above, when an ssh connection is made like so: $ ssh remote-host-nickname The -J flag provides flexibiltiy for easily specifying proxy and remote hosts as needed, but if a specific bastion host is regularly used to connect to a specific remote host, the ProxyJump configuration can be set in ~/.ssh/config to automatically make the connection to the bastion en-route to the remote host: # The Bastion Host For example, a public bastion host giving access to a "web tier" set of hosts, within which is a further protected "database tier" group might be accessed. This feature is useful if there are multiple levels of separation between a bastion and the final remote host.
SSH PROXY SERVER WINDOWNS SERIES
The ssh man (or manual) page ( man ssh) notes that multiple, comma-separated hostnames can be specified to jump through a series of hosts: $ ssh -J, You can also set specific usernames and ports if they differ between the hosts: $ ssh -J
SSH PROXY SERVER WINDOWNS PLUS
To use it, specify the bastion host to connect through after the -J flag, plus the remote host: $ ssh -J The ProxyJump, or the -J flag, was introduced in ssh version 7.3. Instead of first SSHing to the bastion host and then using ssh on the bastion to connect to the remote host, ssh can create the initial and second connections itself by using ProxyJump. The ssh command has an easy way to make use of bastion hosts to connect to a remote host with a single command.

Linux system administration skills assessment.A guide to installing applications on Linux.
SSH PROXY SERVER WINDOWNS DOWNLOAD
Download RHEL 9 at no charge through the Red Hat Developer program.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
